In 2019, orders for electrical vehicles (EVs) amounted to more than two million. Which is twice the volume sold two years ago. Experts have predicted the order will rise to 245 million vehicles by the year 2030.
When attention is shifted to electric cars to reduce the rising rate of carbon dioxide emissions. The car manufacturers are increasing the number of electric vehicle offerings according to New innovations to create sustainable electricity sources to power those vehicles. The installation of a solar charging station is therefore imperative to ensure energy sustainability meets future needs.
What is EV?
EV or Electric Vehicle is a vehicle that uses electrical energy to drive. Can be charged continuously. When the battery is dead the work of an EV electric system has a slightly different working principle. It depends on the type of EV. In general, people are paying attention to electric vehicles such as BEV, Battery Electric Vehicle, which is the most efficient use of electric energy to drive a vehicle. Operation starts from battery Which is the power source of the system that stores DC power Will be Inverter draws energy from the battery to convert to AC power and forward it to the motor. To enable the car to move.
Electric drive can make the car move quietly and smoothly. Like a car moving with fuel energy Which makes it more cost-effective Both maintenance costs and the cost of energy that electricity will cost less than fuel energy. Moreover, this electric car Can respond to your driving with the desired acceleration because the electric motor immediately commands the drive. And also friendly to the environment There is no exhaust emission, so it does not pollute the world.
Electric-powered vehicles can be divided into 4 types
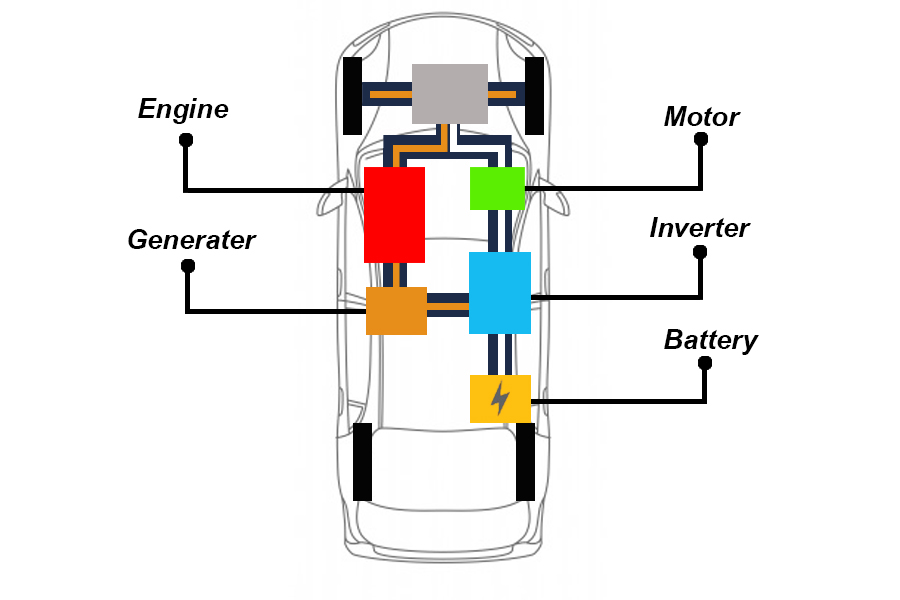
1. Hybrid electric vehicle (HEV)
These are vehicles that contain both a conventional fuel-powered engine and an electric motor with a battery. Which is halfway between the fuel-powered vehicles and electric vehicles Therefore, it has lower fuel consumption than normal vehicles. And it can also bring the remaining mechanical energy or not be converted into electrical energy stored in the battery. Vehicles of this type do not have a plug socket to charge electricity. Electric energy is generated by driving cars with fuel energy.
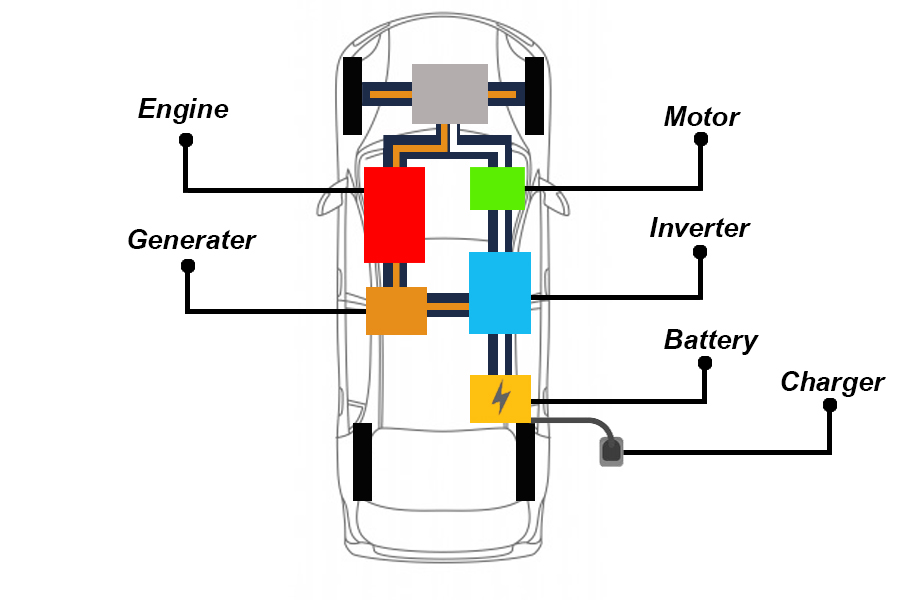
2. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
Vehicles developed from Hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) models have the function of driving with fuel energy. And the operation of electric drive by adding a plug-in system So that it can be charged from the outside and stored in the battery.
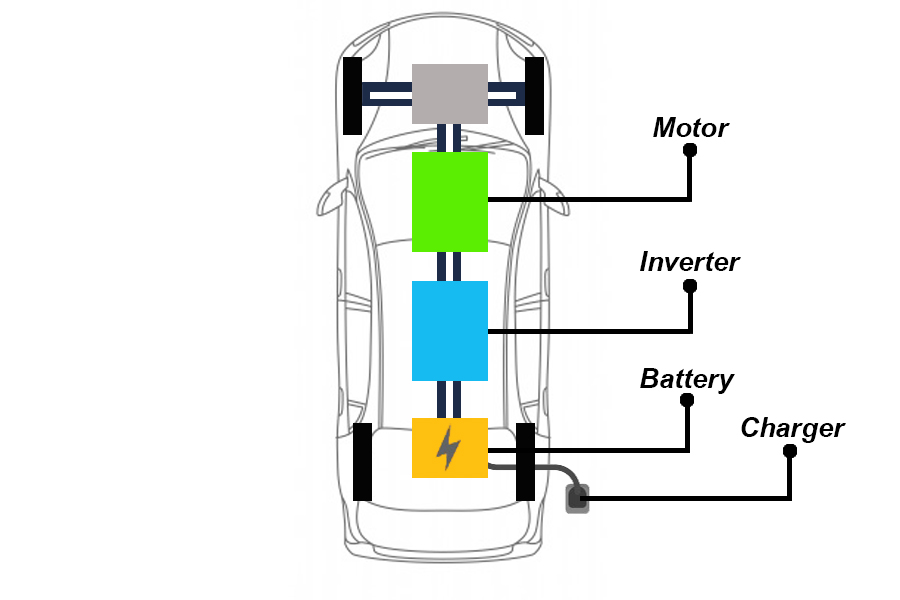
3. Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
100% electric-powered vehicles with plug-in system allow external charges to be stored in the battery. Inverter is available to convert electricity bills and send them into motors, allowing the vehicle to move. This type of vehicle supports the use of electric batteries, which comes only from plugging in electric chargers.
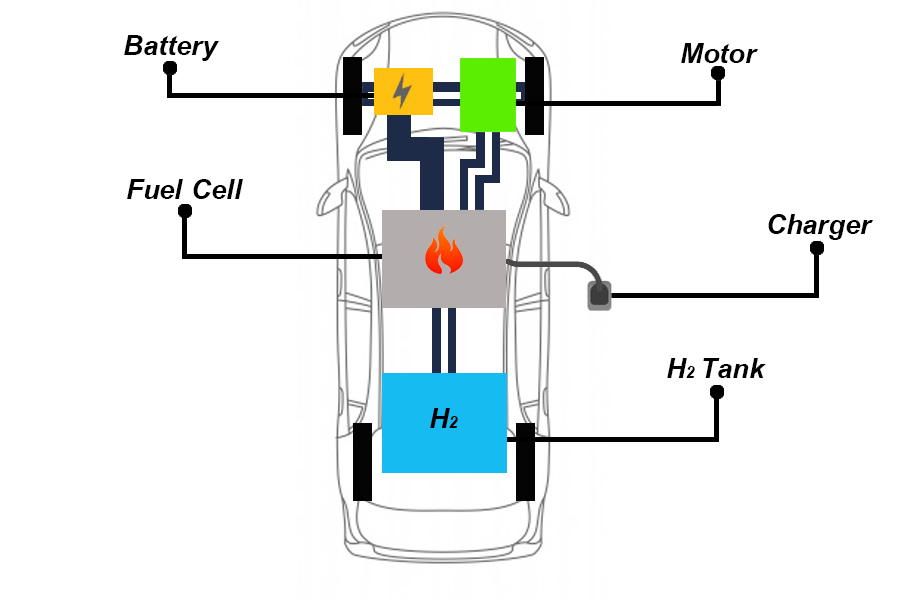
4. Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
100% electric-powered vehicles with plug-in system allow external charges to be stored in the battery. Inverter is available to convert electricity bills and send them into motors, allowing the vehicle to move. This type of vehicle supports the use of electric batteries, which comes only from plugging in electric chargers.
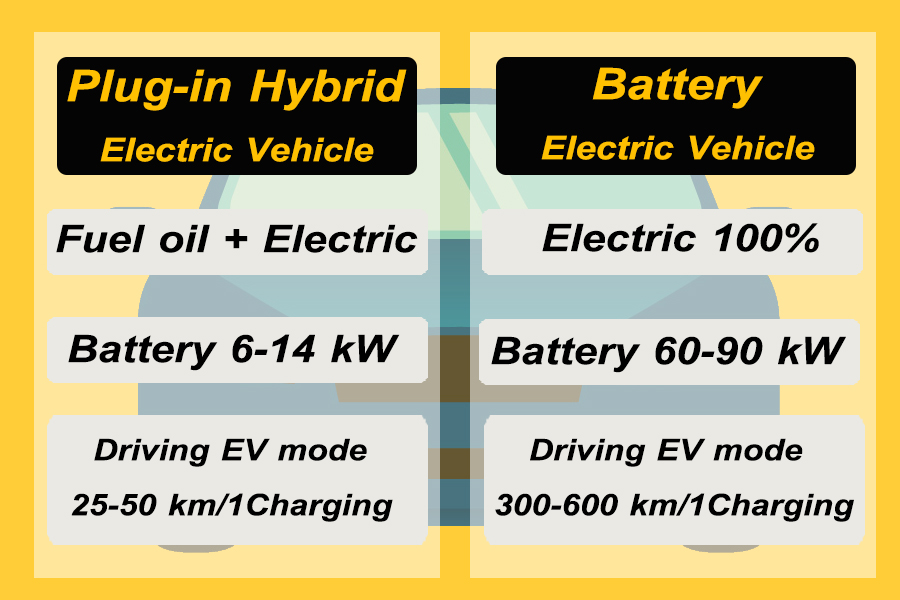
Consider the possibilities of driving electric vehicles. Produced from solar energy with the power requirements of electric vehicles Regarding the type of Electric Vehicle you choose, the vehicle’s battery system. Travel distance And charging time in general, an EV that uses 100% electricity has a battery capacity of 60-90 kWh, can run at a distance of 300-600 km / 1 charge.
Electric Vehicles (EV) has a kilowatt-hours (kWh) it takes for the car to drive 100 miles. The amount of Solar Panels suitable for an installation to generate electricity for an EV depends on the daily distance driving a vehicle. Weekly or monthly If you live in a dense urban area Short trips, the number of Solar Panels required will be less than the longer trips for suburban dwellers.
Besides a solar panel, it also needs a battery storage system to support it, as most families rely on overnight EV charging when the sun isn’t shining, working with a charging station. Where you can plug-in your car.
EV Charging
EV charging is divided into 2 types
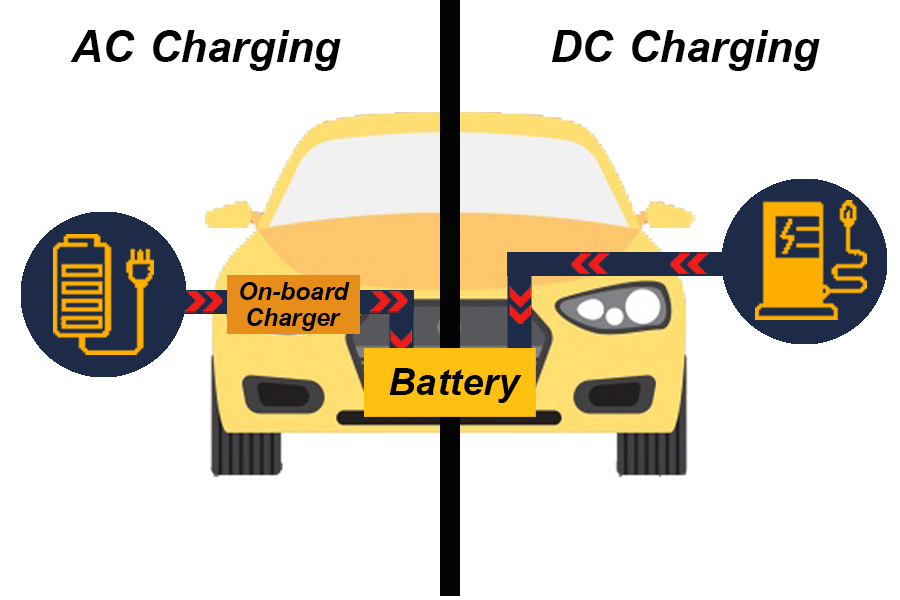
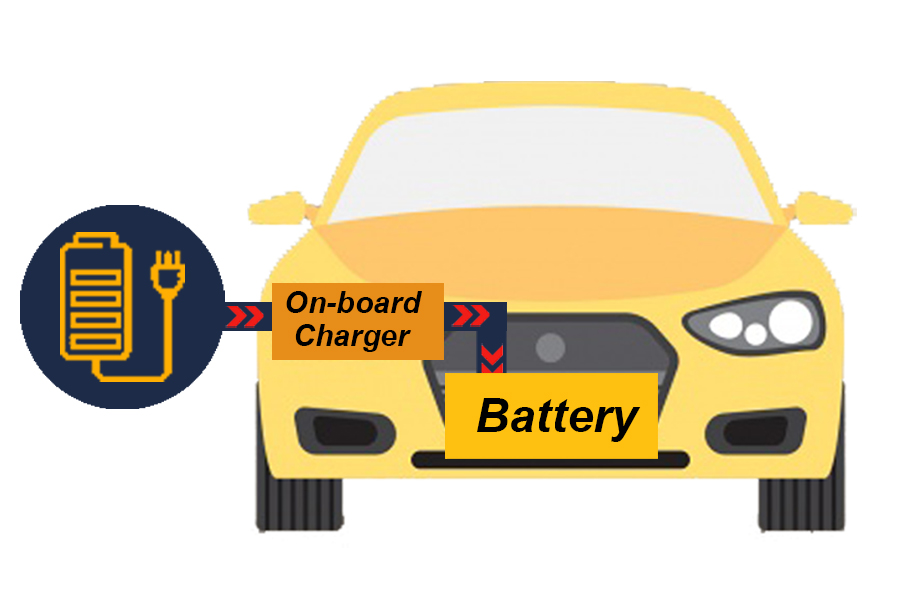
1. Normal Charge หรือ Home EV Charger
Typical charging, AC charging via Portable EV Charger is included with a head on one side for plugging into the car’s charging port. And the other side will be a power outlet can be used with a home outlet The electric charge that is injected into the vehicle is charged through the on board Charger inside the electric vehicle Which is responsible for converting AC power to DC power which charges electric charges. And the size of the on board charger depends on the brand of the car, which the size of the on board charger will affect the charging time of the car battery.
2. Quick Charge
Quick charge uses the electric vehicle charger to convert to DC power, and the DC power directly enters into the electric vehicle battery for charging. According to the auto manufacturer’s standard, the standardized charger, electric booster socket will be used as AC and DC charger.
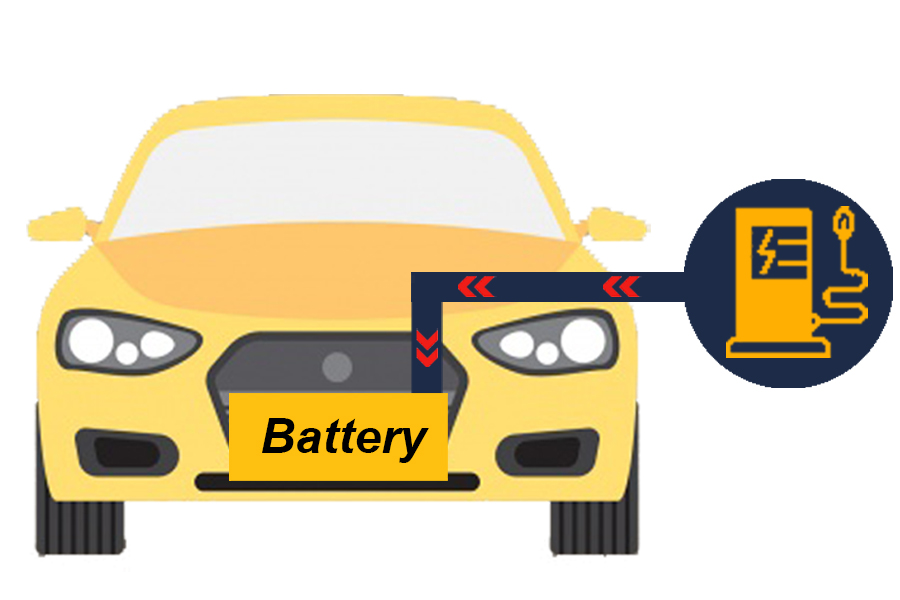
EV Charging by Solar Energy
This type of charging can be charged in a personal residence. If the residence is equipped with Electric Systems to generate electricity from solar energy. Will be able to draw that electricity that is produced Can be charged to the Electric Vehicle (EV) by charging DC electricity directly from the Solar Panel into the car’s battery without having to go through the On Board Charger to convert electricity. Substances reduce the charging time. And can help save energy costs on vehicle charging.
Installing an EV Charger connected to a solar panel is another interesting option. For reducing the time spent in the EV charging And use 100% natural clean energy. The use of electricity produced from solar energy. Will not cause pollution Which is the cause of current environmental problems.
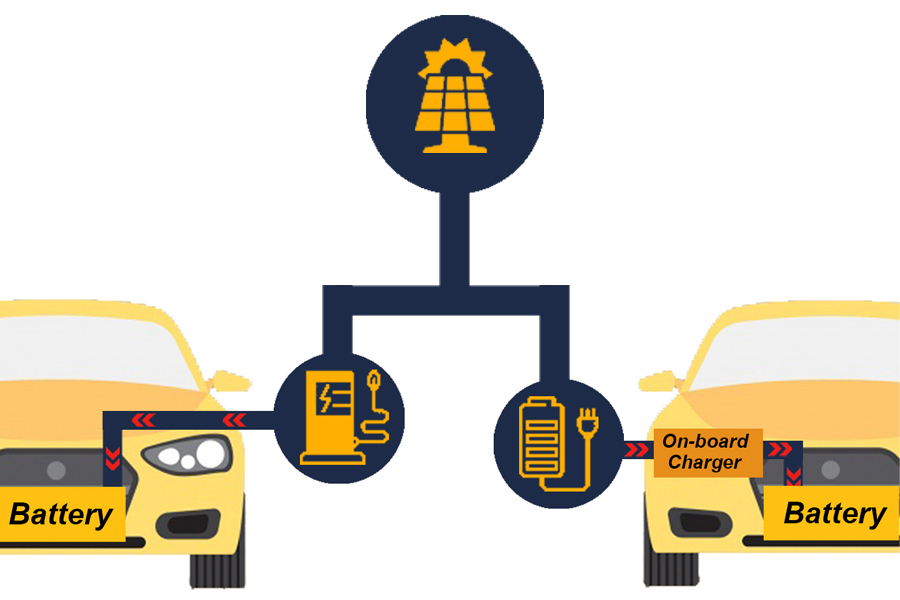
Even assuming that the price of gas remains steady over the next quarter of a century (which it surely will not), you could expect to save upwards of 372,600 Baht ($12,000) over 25 years, even after factoring in the costs of installing a solar-powered EV charging system. If you were to incorporate a solar power EV system to an already existing residential solar array, the costs would even be lower.